In German, there are two types of passive: Process Passive (Vorgangspassiv) and Status Passive (Zustandspassiv). They have different meanings, constructions, and uses. In this lesson we focus on the status passive.
The Status Passive (Zustandspassiv)
In the Vorgangspassiv, the focus is on the action. In the status passive, the action has already been completed, and the focus is on the status after the action. Therefore, only verbs that result in a change of status can be put into the status passive voice.
Who does the action and causes the change in status is not important.
Examples:
- „Die Frau wurde angefahren. Sie ist verletzt.“
The „anfahren“ action is already completed here. During the action the woman was injured.
⇒ Her current condition: She is injured.
⇒ Who hit the woman again does not matter or is unknown.
Constructing the Zustandspassiv
Present Tense
It's made of two parts:
sein + past participle
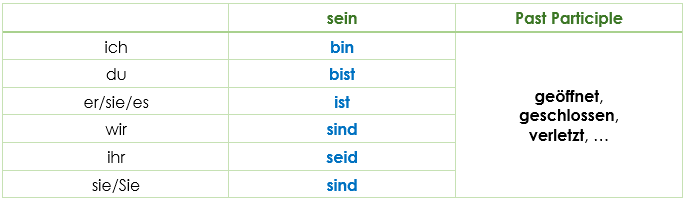
Example:
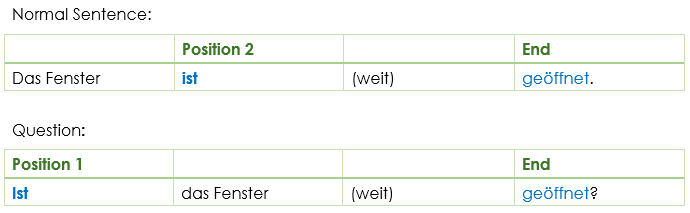
- „Das Fenster ist geöffnet.“
"Sein" is conjugated and the past participle goes at the end of the sentence.
With Modal Verbs
It's made of three parts.
modal verb + past participle + sein
Example:
- „Das Fenster muss geöffnet sein.“
The modal verb is conjugated and "sein" goes at the end of the sentence. The past participle goes in the second to last position.
Zustandspassiv in All Tenses

It is impossible to form the status passive in any other tense.
Examples of the Zustandspassiv
Present:
- „Der Mann ist schwer verletzt."
- „Der Zaun ist frisch gestrichen."
Simple Past:
- „Der Mann war schwer verletzt."
- „Der Zaun war frisch gestrichen."
Future 1:
- „Der Mann wird schwer verletzt sein."
- „Der Zaun wird frisch gestrichen sein."
Special offer: 5 Ebooks for Free!
Do you like EasyDeutsch? When you buy my Ebooks, you get exercises and even more simple, easy-to-understand explanations, and you also actively support me. Right now there is an offer where you get all 10 EasyDeutsch ebooks for the price of 5 ebooks! Get my ebooks today at a special price: Yes, I want the ebooks and over 100 bonus lessons!
Word Order in Zustandspassiv
Gramato: Your German Grammar Coach
Try Gramato now!
Powered by EasyDeutsch AI

This is how Gramato can help you!
Gramato helps you with all your German grammar questions – fast, to the point, and always based on the trusted content from https://easy-deutsch.com.
Gramato offers fill-in-the-blank exercises on a variety of grammar topics, tailored to your level so you can practice exactly what you need.
Get answers in multiple languages – German, English, Spanish, French, and more. That way, you can understand grammar in the language you feel most comfortable with.
Clear and simple grammar explanations – so you can learn faster and smarter with Gramato.
Ask your questions or practice anytime with Gramato – no wait, just results!
Related Topics:
Entire lesson in German only: Zustandpassiv
You can find more lessons on Verbs here:
- Was sind Verben? (What are Verbs?)
- Starke Verben (Strong Verbs)
- „sein“ und „haben“ ("sein" and "haben")
- Reflexive Verben (Reflexive Verbs)
- Trennbare & Untrennbare Verben (Separable & Inseparable Verbs)
- Modalverben (Modal Verbs)
- Partizip 1 (Present Participle)
- Partizip 2 (Past Participle)
- Das Verb „werden” (Verb "werden")
- Das Verb „lassen” (Verb "lassen")
- Imperativ (Imperative)
- Konjunktiv 1 (Subjunctive 1)
- Konjunktiv 2 (Subjunctive 2)
- Das Passiv (Passive Voice)
- Vorgangspassiv (Process Passive)
- Das Passiv in allen zeitformen (Process Passive in all tenses)
- Verben ohne Passiv (Verbs without Passive voice)
- Das unpersönliche Passiv (Impersonal Passive)
- Verben mit Ergänzungen (Verbs with Complements)
- Verben mit Nominativ (Verbs with Nominative)
- Verben mit Akkusativ (Verbs with Accusative)
- Verben mit doppeltem Akkusativ (Verbs with double Accusative)
- Verben mit Dativ (Verbs with Dative)
- Verben mit Akkusativ & Dativ (Verbs with Accusative & Dative)
- Verben mit Genitiv (Verbs with Genitive)
- Verben mit Präpositionen (Verbs with Prepositions)
Lists on the topic of German verbs:
- Die 30 wichtigsten Verben mit Vokalwechsel (The 30 most important verbs with vowel change)
- Untrennbare Präfixe (Inseparable Prefixes)
- Wechselpräfixe (Two-case Prefixes)
- Unregelmäßige Partizip 2 Formen (Irregular Participle 2 forms)
- Nomen-Verb-Verbindungen (Noun-Verb compounds)
You can find an overview of all topics under German Grammar.
Recommendation: Free video lessons every Tuesday & Thursday
Sign up now: Email German Grammar course


