What is the German Simple Past Tense (Präteritum)?
In German, there are two different tenses we can use to talk about he past: the Simple Past Tense (Präteritum) and the Perfect Tense (Perfekt).
They both mean the same thing (something happened in the past), but we use them in different circumstances (in general: the simple past when writing, the perfect when speaking).
Examples of the German Simple Past Tense:
- „Das Wetter war schlecht.“
- „Er machte Urlaub.“
- „Wir hatten Glück.“
How to Construct the Simple Past Tense (Präteritum)?
Conjugation - Regular Verbs
Regular verbs are conjugated by removing the "-en" ending and replacing it with another ending (based on the subject of the sentence):

Special Features:
If the verb stem ends in „-d“ or „-t“ add an „e“ before the ending.
Example with „arbeiten“:
- „ich arbeitete“,
- „du arbeitetest“,
- „er arbeitete“, …
Conjugation - Strong (Irregular) Verbs
Verbs that have a vowel change are called strong verbs. These are normally the same verbs that are irregular in the present tense, but not always!
In plural, they often use the German Simple Present (Präsens) endings.
In the first and third person singular, they often have no ending (the first and third person singular are always identical to each other, for both regular and irregular verbs).
Examples for irregular verbs:
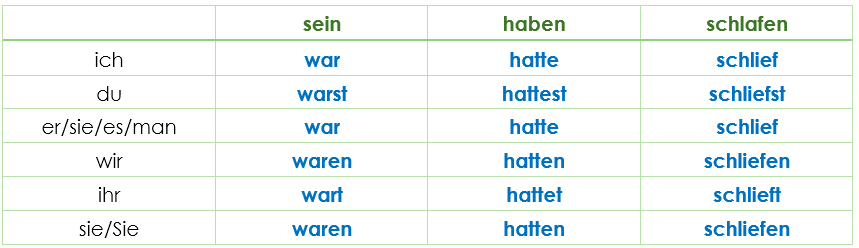
Bad News for German Learners
About 50% of all verbs are irregular in the simple past!
Even some Germans don‘t know the conjugations of all verbs in the simple past.
When possible, they try to avoid using them. And you should to!

Special offer: 5 Ebooks for Free!
Do you like EasyDeutsch? When you buy my Ebooks, you get exercises and even more simple, easy-to-understand explanations, and you also actively support me. Right now there is an offer where you get all 10 EasyDeutsch ebooks for the price of 5 ebooks! Get my ebooks today at a special price: Yes, I want the ebooks and over 100 bonus lessons!
When to use the German Simple Past Tense (Präteritum)?
For completed actions in the past:
- „Er war letztes Jahr in Deutschland.“
- „Ich ging gestern ins Theater
For facts and conditions about the past.
- „Das Wetter war gut.“
- „Deutschland wurde 1990 Fußballweltmeister.“
But aren't those the same times we use the Perfect Tense?!?!? Yep! The simple past and the perfect have the same meaning. The difference is that we use the simple past when writing (especially formal writing) and the perfect when speaking.
Exception: Modal Verbs, Sein and haben almost always use the simple past (even when speaking).
Perfect Tense (Perfekt) or Simple Past Tense (Präteritum)?

Rule of thumb: when speaking, if you aren't sure, use the German Perfect Tense.
Gramato: Your German Grammar Coach
Try Gramato now!
Powered by EasyDeutsch AI

This is how Gramato can help you!
Gramato helps you with all your German grammar questions – fast, to the point, and always based on the trusted content from https://easy-deutsch.com.
Gramato offers fill-in-the-blank exercises on a variety of grammar topics, tailored to your level so you can practice exactly what you need.
Get answers in multiple languages – German, English, Spanish, French, and more. That way, you can understand grammar in the language you feel most comfortable with.
Clear and simple grammar explanations – so you can learn faster and smarter with Gramato.
Ask your questions or practice anytime with Gramato – no wait, just results!
Related Topic:
Entire lesson in German only: Präteritum
More lessons about Tenses:
- Perfekt (Perfect Tense)
- Präsens (Present Tense)
- Plusquamperfekt (Past Perfect Tense)
- Futur 1 (Future 1)
- Futur 2 (Future 2)
What is the general German word order? - Satzbau (Sentence Structure).
You can find an overview of all topics under German Grammar.
Recommendation: Free video lessons every Tuesday & Thursday
Sign up now: Email German Grammar course


